Tungsten Market Evolution and Key Applications
Initially a niche material for incandescent filaments, tungsten’s role expanded rapidly after the 1927 development of tungsten-carbide hardmetals, and its strategic value surged in World War II through armour-piercing projectiles and high-speed cutting tools. Over the past several decades, leadership in the global tungsten market shifted from Western nations to China as manufacturing globalised and environmental regulations tightened, making China the dominant force in the industry.
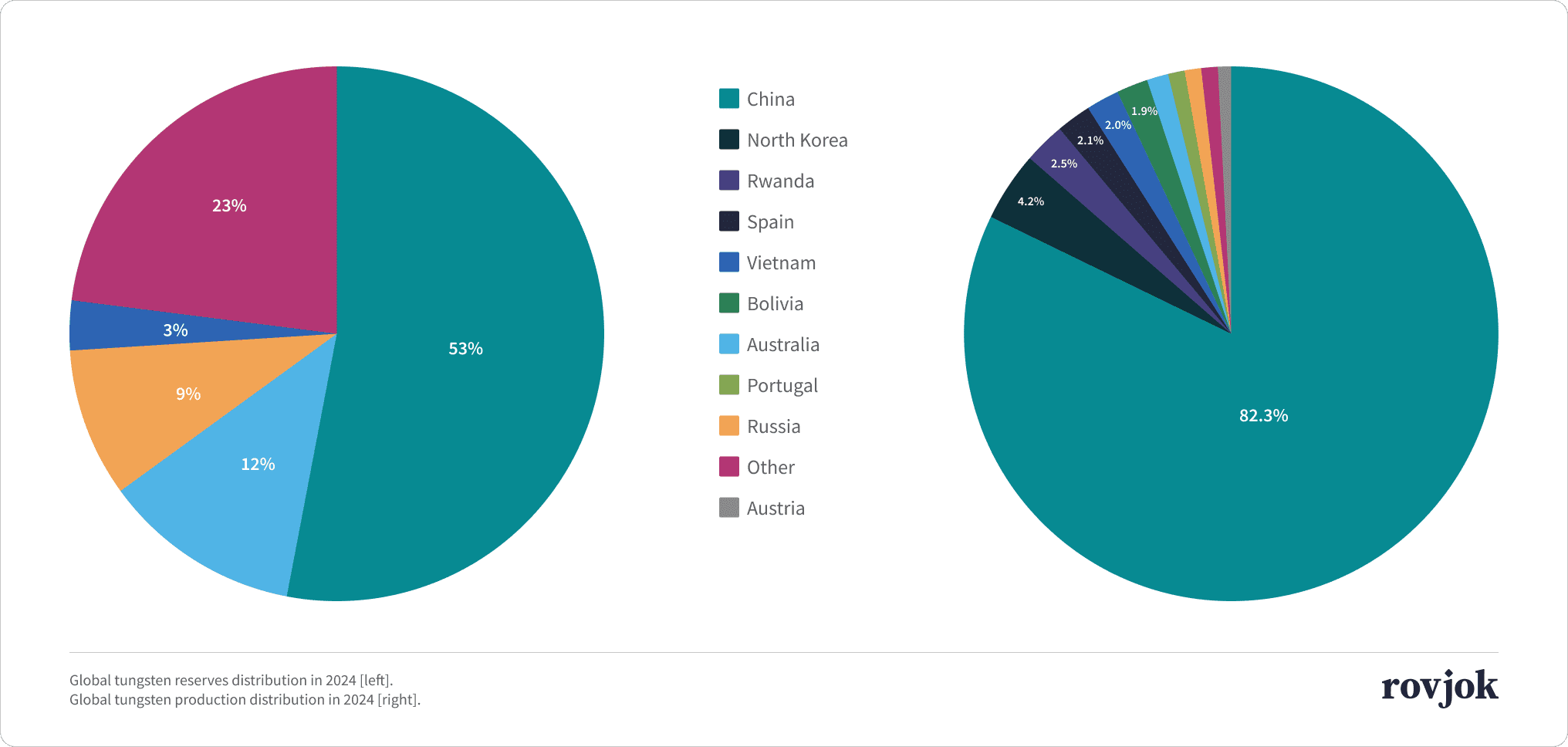
Global tungsten reserves distribution in 2024 [left]. Global tungsten production distribution in 2024 [right].
Today tungsten is regarded as a highly strategic critical mineral for defence, with primary value delivered through alloyed and composite forms. Tungsten carbide in cemented carbides is the largest end use, providing cutting, drilling, and wear-resistant tooling across manufacturing and mining. Additional applications include alloy steels for high-temperature machining, superalloys for jet engines and gas turbines, and high-density alloys for penetrators, radiation shielding, and counterweights. Beyond these, uses span energy, aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, including silicon-wafer cutting wires, high-voltage electrodes, and filament lamps. Consequently, any credible tungsten market analysis must link end-use growth to the tungsten supply chain and recognise how these applications shape the broader tungsten market.